-
article · 2026Year28Moon3Day
Opentrons Flex 的节省成本优势与投资回报分析
Read More -
article · 2026Year24Moon3Day
使用 Opentrons Flex 降低 NGS 文库制备误差的方法
Read More -
article · 2026Year8Moon2Day
高通量 NGS 自动化技术趋势:Opentrons Flex 的作用
Read More


Pipettes, as indispensable precision tools for liquid transfer in the laboratory, are often required to handle the transfer of viscous liquids. However, the unique physical properties of viscous liquids, such as high viscosity and easy adhesion, undoubtedly add a lot of difficulty to the precise operation of pipettes. To ensure efficiency and accuracy when pipetting such liquids, effective methods for pipetting viscous liquids are detailed below.
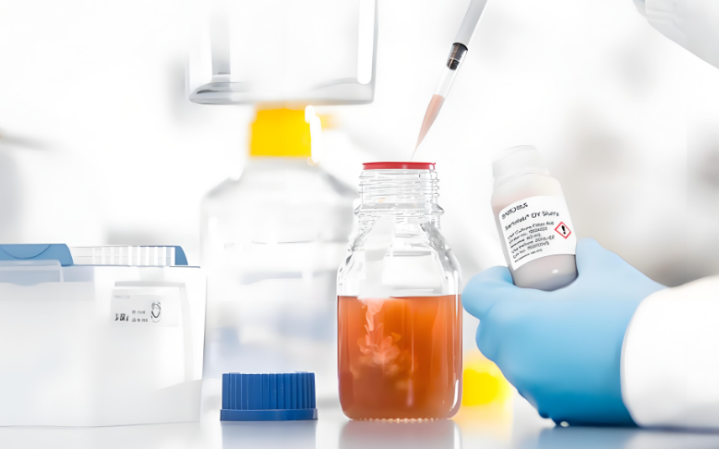
1. Operation method 1. Choose a suitable pipette: (1) According to the experimental needs, select a pipette with an appropriate range. (2) For viscous liquids, you may need to choose a pipette with a larger capacity to cope with the additional resistance brought by the viscous liquid. 2. Adjust the pipette settings: (1) Ensure that the pipette's volume setting is correct to avoid leakage or insufficient suction caused by improper volume range. 3. Pre-wet the suction head: (1) Before absorbing viscous liquid, pre-wet the inside of the suction head with a small amount of liquid to reduce the adsorption force of the viscous liquid to the suction head and improve the suction efficiency. (2) The tip can be pre-wetted by repeatedly sucking the liquid several times. 4. Use the reverse pipetting method: (1) For high-viscosity liquids, it is recommended to use the reverse pipetting method. (2) First press the button to the second stop point, and then slowly release the button to the origin so that the tip is filled with more liquid than the set range. (3) When transferring liquid, just press the button to the first stop point to discharge the liquid with the set range without blowing out the remaining liquid. 5. Control the aspiration speed: (1) When absorbing viscous liquids, the aspiration speed should be appropriately controlled to avoid excessive liquid backflow into the tip cone or into the interior of the pipette.
2. Precautions 1. Keep the pipette, tip and liquid at the same temperature: temperature differences may cause changes in liquid viscosity and affect the pipette's suction effect. 2. Avoid air bubbles in the tip: Air bubbles will affect the accuracy of pipetting, so when absorbing viscous liquids, make sure there are no bubbles in the tip. 3. Replace the tip regularly: The tip may become worn or deformed after being used for a period of time, affecting the pipetting effect. Therefore, new suction tips should be replaced regularly. 4. Clean and maintain pipettes: After use, pipettes and tips should be cleaned in time to avoid clogging or contamination with residues. When cleaning, you can use pure water or appropriate detergent to rinse. 5. Pay attention to the operating specifications: When using the pipette, you should follow the operating specifications to avoid leakage or damage caused by improper operation.
When pipetting a viscous liquid, you need to choose a suitable pipette, adjust settings, pre-wet the tip, use the reverse pipetting method, control the pipetting speed, etc. At the same time, you also need to pay attention to maintaining a consistent temperature, avoiding air bubbles, regularly changing tips, cleaning and maintaining pipettes, and following operating specifications. These measures will help ensure the accuracy and efficiency of the pipette and improve the reliability of experimental results.
Related reading recommendations
Thermal oscillation module GEN1 instruction manual
Why automated nucleic acid preparation is needed
The composition of Opentrons magnetic modules
Non-contact liquid workstation
The working principle and characteristics of continuous pipettes
The experienced service team and strong production support team provide customers with worry-free order services.

简体中文

繁體中文

English

日本語

한국인